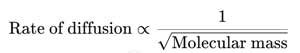Deuterium - and the vital importance of Vapour Permeability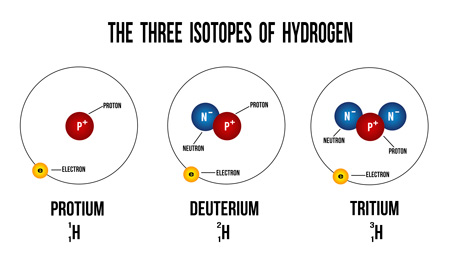
What Vapour Permeability Means
- Vapour permeability is a measure of how easily a gas or vapour can pass through a solid material.
- For deuterium, this usually means the ability of D₂ (molecular deuterium) or deuterium-containing compounds (like heavy water, D₂O) to diffuse through membranes, coatings, or structural materials.
Uses of Vapour Permeability in Deuterium Applications
- Nuclear Fusion Research
- Deuterium is a fuel candidate for fusion (along with tritium).
- Vapour permeability of containment materials (metals, ceramics, polymers) is crucial to:
- Prevent leakage of deuterium fuel.
- Predict diffusion rates in reactor walls or plasma-facing components.
- Manage isotope separation (D vs. T).
- Isotope Separation & Enrichment
- Certain membranes are designed to selectively allow hydrogen or deuterium to pass through.
- Vapour permeability data helps design permeation membranes used in:
- Producing heavy water (D₂O).
- Separating hydrogen isotopes for research or industrial uses.
- Fuel Cells & Electrolysers
- Proton-exchange membranes (like Nafion) can transport hydrogen isotopes.
- Vapour permeability influences how well deuterium ions move through membranes in isotopic studies and in testing durability of fuel cell materials under different isotope loads.
- Cryogenics & Storage
- Deuterium gas is stored at low temperatures and high pressures.
- Vapour permeability of storage vessels determines:
- Leak rates.
- Material compatibility.
- Long-term stability of deuterium supplies.
- Material Science & Safety
- In research labs, knowing the vapour permeability helps prevent deuterium leakage (important for safety and cost reasons).
- Helps assess hydrogen embrittlement effects since deuterium, like hydrogen, can diffuse into metals and alter their mechanical properties.
Importance of Vapour Permeability with Deuterium
- Containment: Prevents loss of expensive and scarce deuterium.
- Efficiency: Ensures that isotope separation, fuel cell processes, or fusion reactors operate with minimal waste.
- Safety: Limits leaks that could pose asphyxiation or flammability hazards.
- Material Selection: Guides engineers in choosing suitable polymers, metals, or ceramics that balance strength with low permeability.
- Fundamental Research: Deuterium’s permeation properties are often studied to model hydrogen transport in materials, since deuterium is easier to trace experimentally.
In short: vapour permeability is critical wherever deuterium must be contained, separated, or transported, from nuclear fusion to fuel cells to isotope chemistry. It directly affects efficiency, safety, and material performance.
Key Differences: Deuterium vs. Protium in Permeability
1. Molecular Mass & Diffusion Rates
- H₂ (protium): Molecular mass ≈ 2 g/mol
- D₂ (deuterium): Molecular mass ≈ 4 g/mol
- Diffusion through materials follows Graham’s Law of Diffusion:
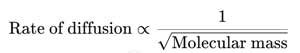
- Therefore:
- D₂ diffuses ~√2 times more slowly than H₂.
- Practically: materials are usually more permeable to H₂ than D₂.
2. Solubility in Materials
- Both H₂ and D₂ dissolve in metals (e.g., Pd, Ni, steel) and polymers.
- D₂ has slightly higher solubility in some metals due to isotope effects (quantum tunneling differences).
- This means that while D₂ diffuses more slowly, it may still accumulate more in certain materials over time.
3. Permeability Trends
- Permeability = Diffusivity × Solubility
- For most metals & polymers:
- H₂ > D₂ in permeability.
- The ratio can vary (typically H₂ permeates ~1.2–2× faster than D₂).
- This difference is exploited in isotope separation membranes.
4. Material Effects
- Metals:
- Hydrogen isotopes can cause embrittlement, but D₂ tends to penetrate more slowly.
- However, once absorbed, D₂ can behave similarly to H₂ in lattice damage.
- Polymers & Membranes:
- Polymers are more permeable to both isotopes, but the slower diffusion of D₂ is useful for selective permeation processes.
- Ceramics:
- Often used in fusion reactors; they show lower permeability for both isotopes, but isotope effects are still measurable.
5. Applications of the Difference
- Fusion Reactors: D₂’s slower diffusion helps reduce losses through reactor walls compared to protium.
- Heavy Water Production (D₂O): Separation processes often rely on the small but significant permeability differences.
- Tracer Studies: Since D₂ diffuses more slowly, researchers use it to track hydrogen transport in materials with higher precision.
Summary Table
Property |
Protium (H₂) |
Deuterium (D₂) |
Molecular Mass |
~2 g/mol |
~4 g/mol |
Diffusion Rate |
Faster |
Slower (~√2 slower) |
Solubility in Metals |
Slightly lower |
Slightly higher |
Permeability Overall |
Higher |
Lower |
Embrittlement Tendency |
High |
Similar but slower onset |
Use in Isotope Separation |
Limited |
Exploited (D/H differences) |
So, while protium permeates more quickly, deuterium’s slower permeation and slightly higher solubility in some materials make it uniquely useful for isotope separation, tracing, and controlled containment in nuclear and energy systems.
About Versaperm - A Complete Range of Solutions
Versaperm offers a broad portfolio of vapour permeability measurement system. Together, these provide a comprehensive approach to tackling many of agriculture’s important – vapour permeability is all too often overlooked but plays a major role in productivity.
Versaperm is a leading specialist in vapour permeability measurement and testing. With decades of expertise, the company provides innovative solutions for industries ranging from agriculture and packaging to pharmaceuticals, construction, and beyond. Its technology enables companies to design, test, and manufacture products that meet the highest standards of quality, performance, and sustainability.